Using mooring anchors to berth ships
Date:2021-03-09
Table of Contents
Berthing a ship safely is one of the most critical operations in port navigation. Mooring anchors play a key role in stabilizing vessels during docking, especially in tidal ports or under windy conditions. This guide explains the ship berthing process, the role of mooring anchors, and practical techniques used by pilots worldwide.
Step-by-Step Ship Berthing Process
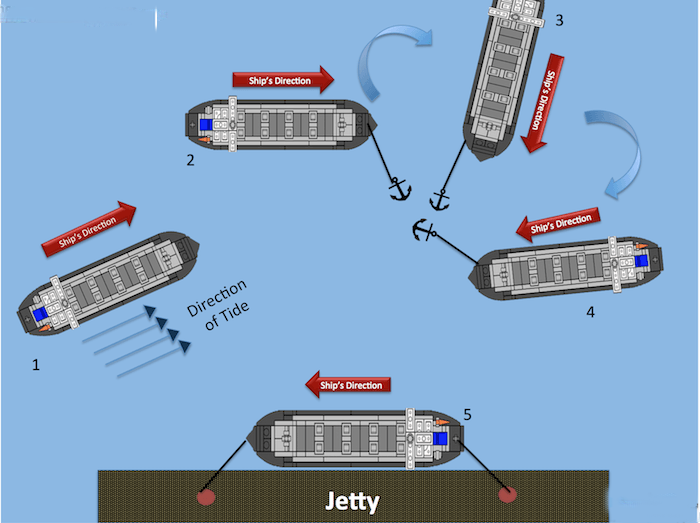
1. Reduce Speed
Before anchoring, reduce ship speed to 3 knots or less.
2. Select Anchor Side
Choose the anchor depending on planned maneuver direction (starboard or port).
3. Pay Out Chain
Chain length should typically be 4–7 times the water depth to maximize holding force.
4. Use Helm & Current
Allow current and helm to swing the ship towards the berth at a 20–25° angle.
5. Final Approach
Secure the vessel using mooring lines and, if available, tugboats.
Types of Mooring Anchors
Different anchor designs are optimized for specific seabed conditions and vessel requirements:
| TUGBOAT TYPE | KEY ADVANTAGE | MAIN APPLICATION |
|---|---|---|
| Stockless Anchor | Compact & easy handling | General use in ports & offshore |
| Fluke / Danforth | High holding in sand & mud | Shallow coastal waters |
| Claw / Bruce | Good reset & stability | Rocky or coral seabeds |
| Plough Anchor | Strong grip in mixed seabeds | Large vessels, varied conditions |
- Anchor Selection Tips
- Consider seabed composition when selecting anchor type
- Match anchor size to vessel displacement and windage
- Always carry appropriate spare anchor components
- Safety Considerations
- Inspect anchor chains regularly for wear and corrosion
- Conduct regular anchor deployment drills with crew
- Monitor weather conditions before anchoring operations
Design and Working Principle
Mooring anchors are designed to provide maximum holding force by creating horizontal pull against the seabed. The anchor chain not only transmits the force but also maintains a catenary effect. This reduces the pull angle, improving anchor efficiency.
In heavy weather, longer chain scope ensures stronger holding and minimizes vessel drift. The catenary effect of the chain absorbs shock loads from wind and waves, protecting both the anchor system and the vessel.
Tugboats and Berthing Assistance
Stern Tug
Controls stern movement during docking, providing lateral stability and precise positioning.
Bow Tug
Assists in aligning the vessel to berth safely, controlling the bow direction and speed.
Escort Tug
Provides extra control for tankers & hazardous cargo vessels through confined waterways.
Emergency Backup
Readily available for rescue or salvage if berthing operations encounter difficulties.
Key Takeaways
Mooring anchors are critical for safe ship berthing, especially under tide and wind conditions.
Proper chain length (4–7 × water depth) ensures maximum anchor holding power.
Tugboats greatly enhance safety and precision during final berthing stages.
Looking for reliable mooring anchors equipment?
- FAQ
What is the role of mooring anchors in berthing?
They stabilize the vessel and prevent drift caused by tide, wind, or current during docking.
How long should the anchor chain be?
Typically 4–7 times the water depth, depending on seabed and weather conditions.
Which anchor type is best for sandy seabeds?
Fluke (Danforth) anchors provide excellent holding power in sand and mud.


